Continuous Mutation of Omicron? ——Characteristics Analysis of BA.2 Variant
I. Crucial virus strain in the new phase of the pandemic progression
The Omicron strain has replaced the Delta strain as the predominant one circulating globally. Although several research teams and laboratories claim to have found recombinant viruses with mixed Delta and Omnicron variants in patients with Coronavirus, the transmissibility and pathogenicity of “Deltacron” is not yet clear, so mutations of the Omnicron strain should be closely monitored. Of the recently reported genetic sequences of new Coronavirus from various regions, 98.3% are the Omicron strain. There are BA.1 1 (B.1.1.529.1), BA.2 (B.1.1.529.2) and BA.3 (B.1.1.529.3) sub-variants of the Omicron family, and the proportion of the BA.2 variant (known as Omicron plus) is increasing and gaining concerns.
The earliest global sample of the BA.2 variant was found in South Africa in November 2021, the numbers of which have been rapidly rising since mid-December 2021. As of February 14, the mutated variant has been found across 74 countries and territories and has become predominantly circulating in 10 countries and territories, including China, Bangladesh, Brunei, Denmark, Guam, India, Montenegro, Nepal, Pakistan, and Philippines. Especially in Denmark, the BA.2 Omicron variant has replaced the original strains as the predominant one in January this year, accounting for the majority in the new cases. As of February 28, the Omicron BA.2 variant accounted for 52% of the new cases in France. On March 10, the French Public Health Agency officially confirmed that the Omicron variant BA.2 as the evolutionary strain of the Coronavirus has become predominant in France.
II. Virological characteristics of the variant BA.2
The Omicron family consists mainly of the BA.1 and BA.2 variants, which have different characteristics. The BA.1 variant shows S-gene target failure (SGTF) in nucleic acid detection, which is an important feature that distinguishes it from the Delta variant, while the BA.2 variant lacks of the genetic features that cause SGTF and is difficult to distinguish during nucleic acid detection. BA.1 has about 60 mutations while BA.2 has about 85 mutations; BA.2 has a total of 28 different mutations from BA.1 and 4 unique mutations in the RBD region; BA.1 has more deletions in N-terminal structural domain while BA.2 has more mutations in the receptor-binding domain. It is found that BA.2 could self-copy in cells faster than BA.1 and is also more likely to produce large-scale fusion cells. The researchers tried infecting hamsters with the BA.2 and BA.1 variants separately and found that hamsters infected with BA.2 were sicker, had poorer lung function, and had more damaged lung tissue samples. However, the pathogenicity of the population needs to be further studied.
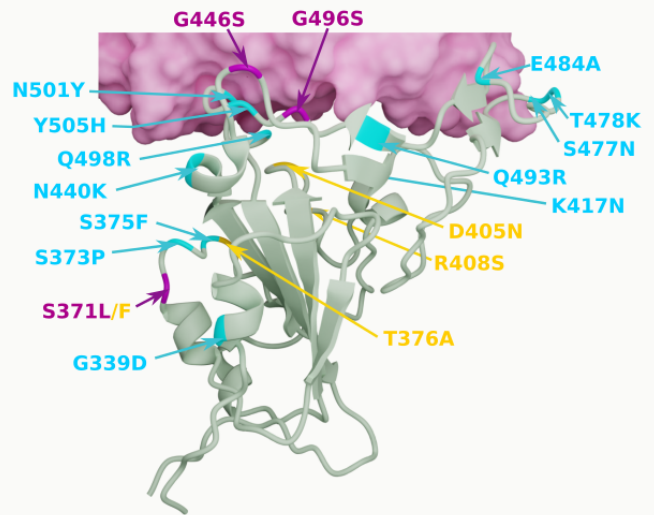
Figure: Mutation sites of BA.2 and BA.1 in RBD (yellow ones are unique to BA.2)
III. Infection transmission characteristics of the variant BA.2
In addition to the unique characteristics of BA.2 in terms of the characteristics of the virus itself, it also has several important features in terms of pandemic transmission that are worth noting as follows:
1. A more transmissible variant
On February 15, WHO noted in its weekly epidemiological report on Coronavirus pneumonia that data from early studies indicated that the Omicron variant BA.2 is more transmissible. The study find that BA.2 is approximately 30% more transmissible than the original strain BA.1. The detection rate of BA.2 is gradually increasing in some areas, and BA.2 is likely to completely replace BA.1. Recently, former WHO officials said that BA.2 may be as highly transmissible as measles, with an R0 index of about 8-15 (the average R0 of measles virus is about 15-18). The recent research results from the HKUMED show that Omicron variants can last on surfaces of glass, plastic, stainless steel and other smooth objects with transmittable virus for 7 days, and its duration of infectiousness is much higher than that of the original strain.
2. Risk of repeat infections
Danish researchers conducted continuous monitoring of patients with positive test result for Coronavirus and confirmed 67 cases of secondary infection. These cases were mostly secondary infections with Omicron variant of Coronavirus within 20 to 60 days, of which 47 cases were infected with BA.1 and BA.2 in succession, and the interval between infections was short. The secondary infections were mainly in the unvaccinated young population and showed only mild symptoms, suggesting that infections induced by the Coronavirus Omicron variants BA.1 and BA.2 are less severe than those by the Delta variants. The study confirms that BA.2 could reinfect patients who have previously recovered from BA.1 infection. And in a British study, 69 patients were found to be reinfected with BA.2 no more than 90 days after their first infection with the Coronavirus, and these patients were predominantly infected with the Delta variant in the previous case.
3. Ability to evade immunity
The Omicron original strain BA.1 already has the breaking-through infectiousness ability. The study found that BA.2 is more capable of evading antibodies immunized by 2 doses of Pfizer vaccine than BA.1, and is more resistant to some therapeutic drugs. BA.2 may have stronger immune evasion properties, which could account for its enhanced transmission ability.
IV. Virus mutation, detection and monitoring
The Coronavirus are RNA viruses with constant mutation, and there is long-term risk of the Omicron variants prevalence. The BA.2 variant does not have the characteristic deletion in the genome that causes S-gene target failure.It is difficult to distinguish from other variant by PCR, and need more complex and time-consuming means such as gene sequencing to clarify.This is why the variant BA.2 is also known as the “Stealth Omicron”.
The World Health Organization (WHO) lists BA.1 and BA.2 together for surveillance, and recently Japanese research and analysis has identified an evolutionary sub-variants of Omicron (BA.1.1) strain. BA.1.1 is a further mutated version of Omicron BA.1, and its infectious properties remain to be seen. A statement from the Israeli Ministry of Health on March 16 said that a mutated variant of the Coronavirus combining features of both Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 sub-variants has been found in travelers, which has not been reported elsewhere in the world, and the possible implications are not yet known.
As the Coronavirus continue to mutate and spread, their detection and prevention cannot afford any carelessness. Effective mutation detection reagents and methods are our powerful weapons to cope with the continuous mutation of the Coronavirus. Sansure Biotech has a full series of solutions for detection of the Coronavirus, including the detection of mutant viruses and second-generation genome sequencing analysis, which can identify the known common Coronavirus mutants to provide strong support for the pandemic prevention and control.
Note: The picture comes from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact the author to delete it.
Disclaimer: All the publications on this website, where the source is indicated, are copyrighted by the original source and do not represent the position of this website.